Integration
INTEGRATION
Introduction:
Integration is a tool
of mathematics to measure area under curve. It is the easiest reverse formula
of Differentiation. Integration comes before differentiation. In early 5th
century when the area was calculated with the imagination of polygons. Leibniz is
the introducer of integration though many says it’s the theory given by Isaac
Newton.
Symbol:
The symbol of Integration
is ∫. The symbol ∫dx, called the differential of the variable of x. ∫ is taken
from a letter which means the summa or sum or total. This means an integral is
a sum of area of infinitesimally small rectangle under the curve, length – f(x)
& width –dx, being considered for integration over the variable x.
Fourier is the first person who
known to use the limits on top and bottom of the integral symbol to mark the
start and end point of integration.
Types: There are two types of
integrations. They are
- Definite
integration
- Indefinite
integration
Definite integration (Definite
integral calculus):
The integral symbol with a & b as the marked limit basically
represents area under the curve f(x) between these two values of the x. This
form of integral is known as the Definite Integral & is the more applied
form of Integration.
Properties of Definite integration:
Definite integral represents the
real world application of integration. Here are few important properties of
definite integration.
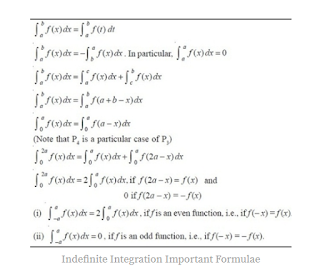 |
| Indefinite integration |
Indefinite Integration (Indefinite
Integral Calculus):
When there are no limits on integral symbol the result of
integration is known as Indefinite integral and is a generalized result of the
area under the curve f(x) for the variable x, where it is continuous.
Properties of Indefinite
integration: Here are some important formula in indefinite integration.
 |
| Definite integration |
Integration formulas:
The integration of function f(x) is
given F(x) and is represented as
∫f(x) dx = F (x) + C
Where, the Right hand side of the
equation means integral of f(x) with respect to x.
F(x) = is called the
anti-derivative or primitive.
f(x) = is called the integrand
dx = is
called the integrating agent
C = is an arbitrary constant is known as the
constant of integration
x
= is the variable of integration




No comments